Mitochondria
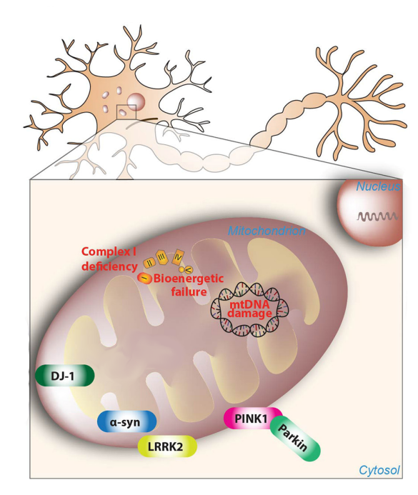
Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cell, and the focus of Mytohealth. These organelles extract nutrients from cells and convert them into ATP, energy currency used by every cell and tissue in the body. While the Y chromosome is passed on from father to son, a mother’s Mitochondria is inherited both sexes. Any dysfunction in mitochondria can lead to long term neurodegenerative disease, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, degradation in muscle movement, memory, and cognition, cardiometabolic systems, and even cancer.
While mitochondria are prone to damage though mutations, ischemia, environment, oxidative stress, and other hazards, they are quickly repaired by a process called “mitophagy”. The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (USP) is responsible for the removal of damaged mitochondria (mitophagy) and also plays a fundamental role in development of new mitochondria, or “mitobiogenesis”.
Mitochondria are the energy factories of the cell, and the focus of Mytohealth. These organelles extract nutrients from cells and convert them into ATP, energy currency used by every cell and tissue in the body. While the Y chromosome is passed on from father to son, a mother’s Mitochondria is inherited both sexes. Any dysfunction in mitochondria can lead to long term neurodegenerative disease, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, degradation in muscle movement, memory, and cognition, cardiometabolic systems, and even cancer.
While mitochondria are prone to damage though mutations, ischemia, environment, oxidative stress, and other hazards, they are quickly repaired by a process called “mitophagy”. The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (USP) is responsible for the removal of damaged mitochondria (mitophagy) and also plays a fundamental role in development of new mitochondria, or “mitobiogenesis”.